HACCP
What is HACCP?

HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) is a process control system that identifies stringent measures to prevent potential hazards and hazards in the food manufacturing process. Strict control of each step of the process reduces the risk of hazards.
This procedures makeup your food safety management based on the seven principle of HACCP.
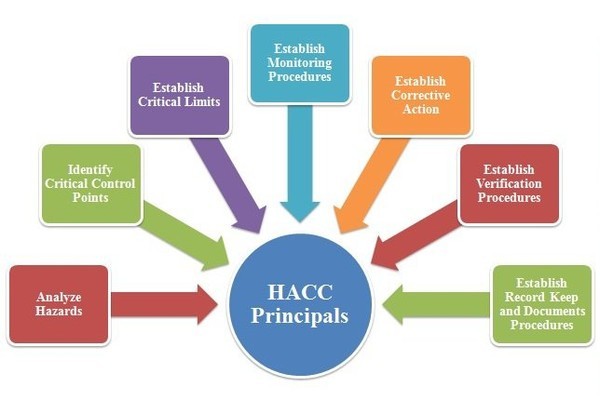
The Seven Principles of HACCP Plan
- Conduct hazard analysis
- Identify critical control points (CCPs)
- Establish critical limits for each critical control point
- Establish critical control point monitoring requirements
- Establish corrective actions
- Establish record keeping procedures
- Keep records for verification
What are 12 Steps of HACCP PLAN?
- Assemble HACCP Team
- Describe Product
- Identify Intended Use
- Construct Flow Diagram
- On-site Confirmation of Flow Diagram
- Conduct a Hazard Analysis
- Determine CCPs
- Establish Critical Limits for each CCP
- Establish a Monitoring System for each CCP
- Establish Corrective Actions
- Establish Verification Procedures
- Establish Documentation and Record Keeping
Why is a HACCP program important?

HACCP is important because it prioritizes and controls potential hazards in food production. By controlling major food risks, such as microbiological, chemical and physical contaminants, the industry can better assure consumers that its products are as safe as good science and technology allows. By reducing food borne hazards, public health protection is strengthened.
Proper implementation of a HACCP program helps reduce the likelihood of customer complaints or a recall by identifying and controlling potential hazards which may come from raw materials, facility processes, and human error. The greater employee awareness that results from a HACCP program helps to drive continual improvement of a company’s products and processes.
- Provides the framework to produce foods safely and to prove they were produced safely.
- Specifically focuses on food safety, not all attributes constituting food quality.
- It is applicable to all phases of food production.
- Focuses on prevention and control of potential food safety hazards rather than inspection.
- Covers all types of potential food safety hazards whether they are naturally occurring in the food, contributed by the environment, or generated by a mistake in the manufacturing process.
- Biological hazards (e.g. bacteria, viruses)
- Chemical hazards (e.g. pesticide residues, and mycotoxins)
- Physical hazards (e.g. metal, glass).
Additionally, the HACCP principles are in alignment with the requirements of the FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) rule for food processors — Hazard Analysis and Risk-based Preventive Controls (“HARPC” or “Preventive Controls”). Although a HACCP plan does not meet all of the requirements, it meets the majority of the requirements and is the best platform from which to build a FSMA-compliant management system.
Get in Touch! Ask us any question/query on +91-9867-180-395. We would be happy to answer your concerns. You can also drop an email at info@ascentinspecta.com
